Complete Guide: Pay Raise Calculator & Salary Strategy (2025)
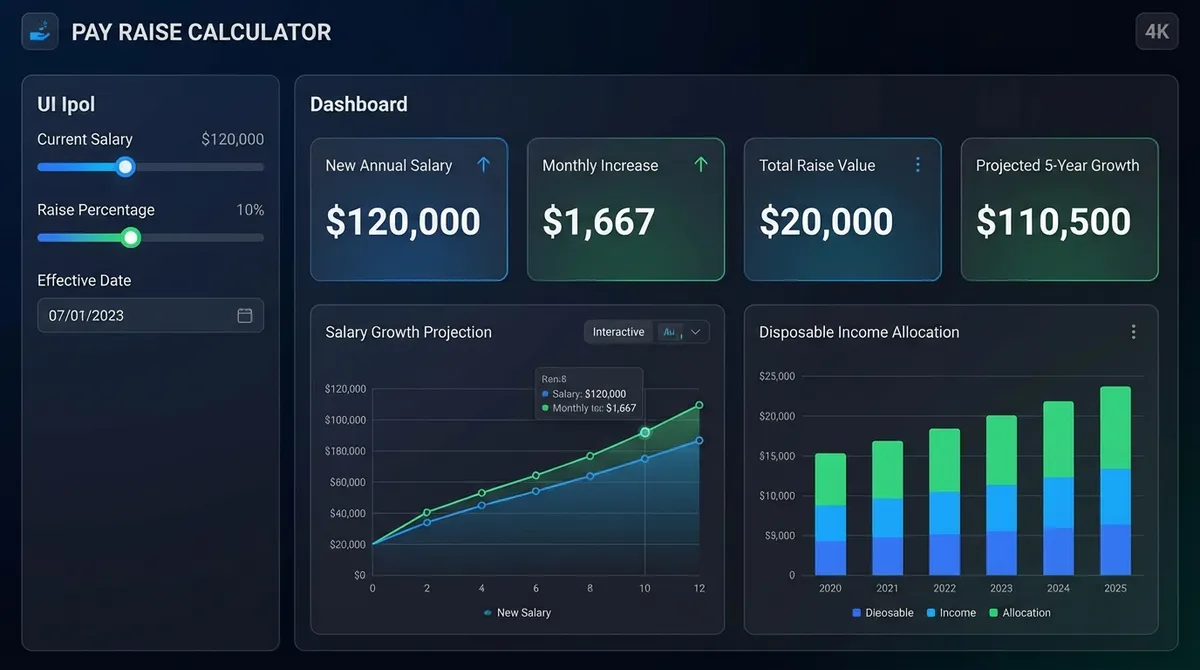
Getting a pay raise is exciting, but seeing the actual impact on your bank account matters more than the percentage on paper. Whether you just secured a 5% merit increase or are negotiating a $5,000 bump for a new role, understanding how that translates to your actual take-home pay is crucial for financial planning.
Why Calculate Your Pay Raise Details?
A "5% raise" sounds simple, but how much is that per paycheck? If you're paid bi-weekly, does it cover your new car payment? Our Pay Raise Calculator breaks down these numbers instantly, converting percentages to dollar amounts and showing you the exact difference across every pay frequency—from hourly rates to annual salaries.
In 2024 and 2025, inflation and cost-of-living adjustments have made salary negotiations more critical than ever. Knowing your numbers empowers you to negotiate with confidence and plan your budget effectively.
How Pay Raises Are Calculated
The math behind a pay raise depends on how the increase is presented: as a percentage of your base salary or as a flat dollar amount.
1. Percentage-Based Raise
This is the most common format for annual reviews. If you earn $60,000 and get a 4% raise:
- Calculation: $60,000 × 0.04 = $2,400 increase.
- New Salary: $60,000 + $2,400 = $62,400.
2. Flat Dollar Amount Raise
Often used in promotions or hiring offers. If you earn $50,000 and get a $3,000 raise:
- Calculation: ($3,000 / $50,000) × 100 = 6% increase.
- New Salary: $53,000.
Understanding Pay Frequencies
One of the biggest confusions with raises is translating an annual bump into a weekly or bi-weekly paycheck. Here is the standard conversion logic used by employers:
Standard Frequency Conversions (Full-Time)
Salary Negotiation Tips for 2025
Negotiating a raise is an art backed by data. Don't just ask for "more money"—present a case centered on value and market reality.
- Know Your Market Rate: Use salary surveys and job postings to find the range for your role in your city. If the average is $75k and you're at $65k, you have a strong data-backed argument.
- Focus on Accomplishments: Document your wins. "I managed a project that saved the company $20k" is infinitely more powerful than "I've been here a year."
- Understand Total Compensation: If the budget is tight, negotiate for reliable non-salary perks like extra PTO, remote work days, or a signing bonus. These have real financial value.
- Use Percentages to Your Advantage: A $5,000 raise might sound big, but if you're earning $150k, it's only 3.3%. Conversely, if you're earning $40k, that same $5,000 is a massive 12.5% jump. Use our calculator to frame your ask in the most favorable terms.
Impact of Inflation (Real vs. Nominal Wage)
It is important to distinguish between your nominal raise (the dollar amount) and your real raise (purchasing power). If you get a 3% raise but inflation is 3.5%, your purchasing power has technically decreased.
When negotiating, citing inflation (which has cooled but still affects costs) helps justify why a generic 2% cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) might not be enough to maintain your current lifestyle.
The "Future Value" of Your Raise
It is easy to underestimate the power of a small percentage increase. Let's look at the math over a 10-year career horizon.
Imagine two employees, Alex and Jordan. Both start at $50,000.
- Alex negotiates a 5% raise every single year.
- Jordan accepts the standard 2% cost-of-living adjustment.
| Year | Jordan (2% Raises) | Alex (5% Raises) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $51,000 | $52,500 | +$1,500 |
| Year 5 | $55,204 | $63,814 | +$8,610 |
| Year 10 | $60,949 | $81,444 | +$20,495 |
Negotiation Scripts That Actually Work
Knowing the numbers is half the battle; communicating them is the rest. Here are three data-driven scripts you can adapt for your next review.
Scenario A: The "Market Adjustment" Ask
Use this when your salary has fallen behind industry standards (inflation or hot market).
"I've been reviewing the market landscape for Senior Analysts in our city. Based on data from [Source], the average compensation has shifted to [Range]. Given my performance this year, specifically [Result 1] and [Result 2], I believe an adjustment to $X would align my compensation with the current market value."
Scenario B: The "Value-Added" Ask
Use this when you've taken on new responsibilities outside your original job description.
"Over the past year, my role has expanded significantly. In addition to my core duties, I've taken ownership of [Project X] and trained [Number] new hires. These additional responsibilities are delivering [Specific Value] to the team. I'd like to discuss adjusting my salary to $X to reflect this increased scope and impact."
Look Beyond the Base: Total Compensation
Sometimes, the budget for salary is truly locked. But that doesn't mean you have to walk away empty-handed. "Total Compensation" includes everything of value your employer provides. Often, these perks are easier for a manager to approve than a base salary hike.
1. Flexibility
Can you negotiate for an extra day of remote work? Or a "Summer Friday" schedule? Time is money. Saving 2 hours of commuting a week is equivalent to a 5% raise in your effective hourly rate.
2. Education & Training
Ask for a budget to attend a conference, take a certification course, or get a degree. This makes you more valuable (and marketable) for your next raise negotiation.
3. One-Time Spot Bonus
If they can't increase your recurring salary, can they offer a one-time signing bonus or retention bonus? This doesn't compound like a salary raise, but it's immediate cash in your pocket.
Look Beyond the Base: Total Compensation
Sometimes, the budget for salary is truly locked. But that doesn't mean you have to walk away empty-handed. "Total Compensation" includes everything of value your employer provides. Often, these perks are easier for a manager to approve than a base salary hike.
1. Flexibility
Can you negotiate for an extra day of remote work? Or a "Summer Friday" schedule? Time is money. Saving 2 hours of commuting a week is equivalent to a 5% raise in your effective hourly rate.
2. Education & Training
Ask for a budget to attend a conference, take a certification course, or get a degree. This makes you more valuable (and marketable) for your next raise negotiation.
3. One-Time Spot Bonus
If they can't increase your recurring salary, can they offer a one-time signing bonus or retention bonus? This doesn't compound like a salary raise, but it's immediate cash in your pocket.
Is a 3% raise good?
A 3% raise is considered standard for a "Cost of Living Adjustment" (COLA) in many corporate environments. It keeps you roughly aligned with average inflation. However, for high performers or those seeking a promotion, a 3% raise is often considered the floor, not the ceiling. Merit increases often range from 4-7%. Ideally, you should aim for a raise that not only covers inflation but also rewards the specific value, new skills, and successful projects you have contributed to the company over the past performance cycle.
How does a raise affect my tax bracket?
A common myth is that a raise can lower your overall take-home pay by pushing you into a higher tax bracket. In the US progressive tax system, only the portion of income above the bracket threshold is taxed at the higher rate. You will almost always take home more money after a raise, though your effective tax rate might inch up slightly.
Pro Tip: The Power of Compounding
Raises compound over time. A $2,000 raise this year increases your "base" for next year's 3% calculation. Negotiating early in your career can add hundreds of thousands of dollars to your lifetime earnings due to this compounding effect.